In this blog post, I demonstrate the creation of a new elasticsearch index with the ability to rollover using the aliases.
We will be implementing the ILM (Information lifecycle Management) in Elasticsearch with Logstash Using Write Aliases
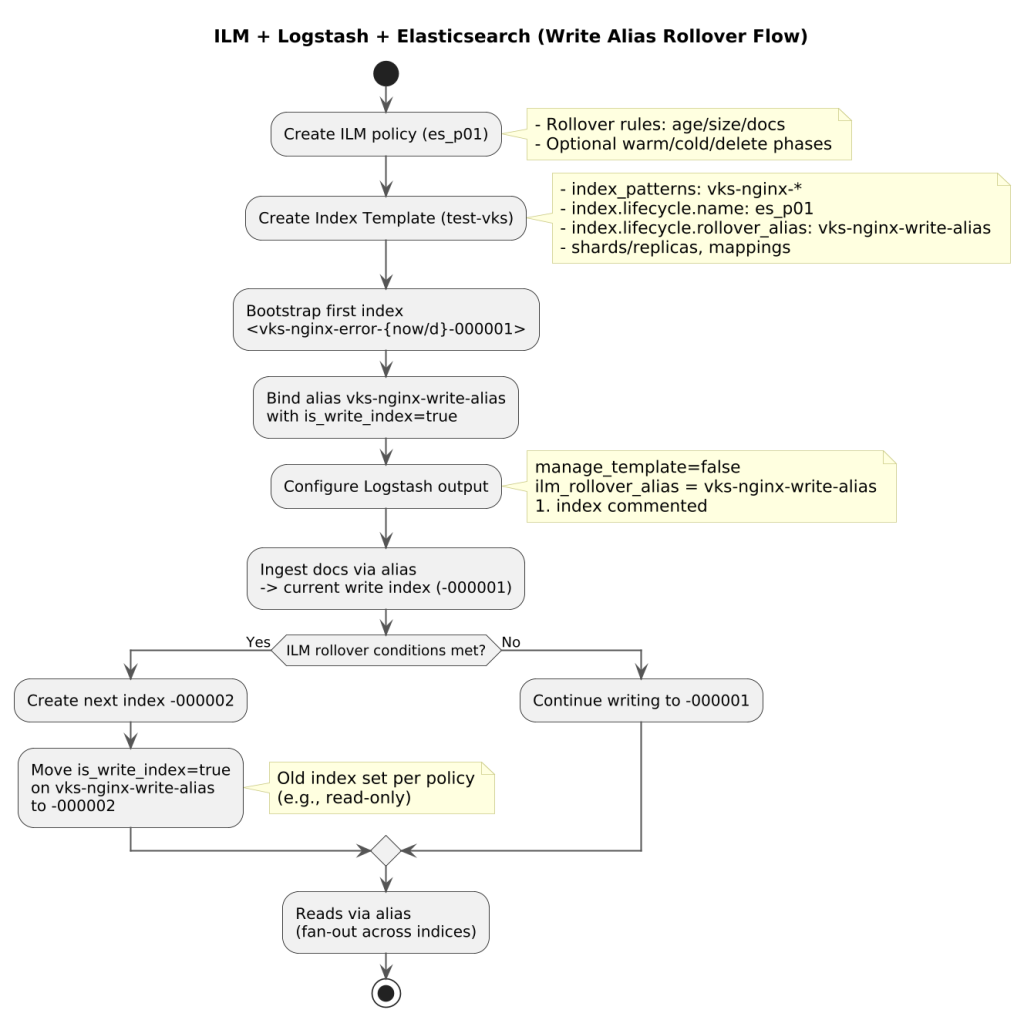
Optimize Elasticsearch indexing with a clean, reliable setup: use Index Lifecycle Management (ILM) with a dedicated write alias, let Elasticsearch handle rollovers, and keep Logstash writing to the alias instead of hardcoded index names. This approach improves stability, reduces manual ops, and scales cleanly as log volume grows.
Implementing ILM with Write Aliases (Logstash + Elasticsearch)
Optimize Elasticsearch indexing with a clean, reliable setup: use Index Lifecycle Management (ILM) with a dedicated write alias, let Elasticsearch handle rollovers, and keep Logstash writing to the alias instead of hardcoded index names. This approach improves stability, reduces manual operations, and scales cleanly as log volume grows.
What you’ll set up
- Write to a single write alias.
- Apply ILM via an index template with a rollover alias.
- Bootstrap the first index with the alias marked as
is_write_index:true. - Point Logstash at
ilm_rollover_alias(not a date-based index).
Prerequisites
- Elasticsearch with ILM enabled.
- Logstash connected to Elasticsearch.
- An ILM policy (example:
es_policy01).
1) Create index template with rollover alias
Define a template that applies the ILM policy and the alias all indices will use.
PUT _index_template/test-vks
{
"index_patterns": ["vks-nginx-*"],
"priority": 691,
"template": {
"settings": {
"index": {
"lifecycle": {
"name": "es_policy01",
"rollover_alias": "vks-nginx-write-alias"
},
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
}
},
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "runtime"
}
}
}
Notes:
- Only set
index.lifecycle.rollover_aliashere; do not declare the alias body in the template. - Tune shards/replicas for your cluster and retention goals.
2) Bootstrap the first index
Create the first managed index and bind the write alias to it.
PUT /<vks-nginx-error-{now/d}-000001>
{
"aliases": {
"vks-nginx-write-alias": {
"is_write_index": true
}
}
}
Notes:
- The
-000001suffix is required for rollover sequencing. is_write_index:truetells Elasticsearch where new writes should go.
3) Configure Logstash to use the write alias
Point Logstash to the rollover alias and avoid hardcoding an index name.
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"]
manage_template => false
template_name => "test-vks"
# index => "vks-nginx-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" # keep commented when using ILM
ilm_rollover_alias => "vks-nginx-write-alias"
}
}
Notes:
manage_template => falseprevents Logstash from overwriting your Elasticsearch template.- Restart Logstash after changes.
How rollover works
- When ILM conditions are met, Elasticsearch creates the next index (
...-000002), moves the write alias to it, and keeps previous indices searchable. - Reads via the alias cover all indices it targets; writes always land on the active write index.
Common issues and quick fixes
- rollover_alias missing: Ensure
index.lifecycle.rollover_aliasis set in the template and matches the alias used in bootstrap and Logstash. - Docs landing in the wrong index: Remove
indexin Logstash; use onlyilm_rollover_alias. - Alias conflicts on rollover: Don’t embed the alias body in the template—bind it during the bootstrap call only.
Quick checklist
- ILM policy exists (e.g.,
es_policy01). - Template includes
index.lifecycle.nameandindex.lifecycle.rollover_alias. - First index created with
-000001andis_write_index:true. - Logstash writes to the alias (no concrete index).
- Logstash restarted and ILM verified.
Verify your setup (optional)
Run these in Kibana Dev Tools or via curl:
GET _ilm/policy/es_policy01 GET _index_template/test-vks GET vks-nginx-write-alias/_alias POST /vks-nginx-write-alias/_rollover # non-prod/manual test